🚀 宇宙の記憶・カレンダー検索
🚀 象徴的な写真:
APOD第1回
🚀 創造の柱
🚀 スピリット火星着陸
🚀 ハッブル超深宇宙
🚀 地球へようこそ|ブルー・マーブル
🚀 エンケラドス
🚀 ベテルギウス
🚀 火星着陸
🚀 青い夕焼け
🚀 冥王星のハート
🚀 皆既日食
🚀 アースライズ再構築
🚀 ブラックホール
🚀 ウェッブ初画像
🚀 アポロ11着陸
APOD30周年(2025年6月16日)
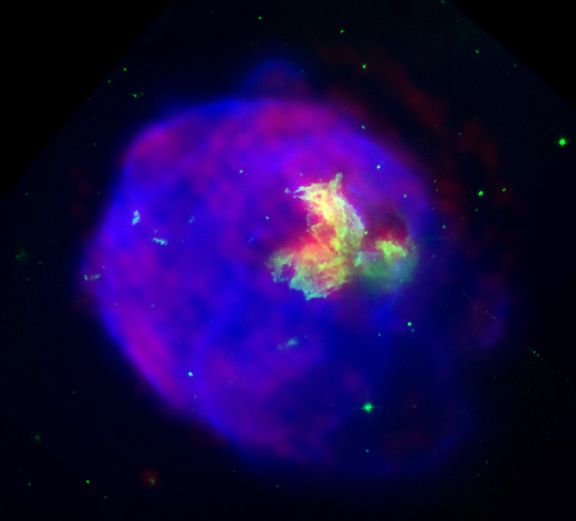
N63Aの構造
Structure in N63A
巨大な恒星爆発の残骸である超新星残骸N63Aのこの擬似カラーの多波長画像には、殻や弧が豊富に見られます。X線放射(青)は、宇宙の爆発で高速移動する物質の塊が周囲の星間物質を巻き込む際に1000万度に加熱されたガスから発せられます。電波放射(赤)と可視放射(緑)は中心領域付近で明るくなっており、X線は拡大する残骸の雲の地球側の密度が高く温度の低い物質に吸収されているように見えます。大マゼラン雲として知られる近隣の銀河に位置するこの超新星残骸の見かけの年齢は2000年から5000年で、その輝きは約60光年に及びます。この興味深い画像は、周回軌道上のチャンドラ天文台のX線データ、ハッブル宇宙望遠鏡の可視データ、オーストラリア・テレスコープ・コンパクト・アレイの電波データを合成したものです。
原文(English)
Shells and arcs abound in this false-color, multiwavelength view of supernova remnant N63A, the debris of a massive stellar explosion. The x-ray emission (blue), is from gas heated to 10 million degrees C as knots of fast moving material from the cosmic blast sweep up surrounding interstellar matter. Radio (red) and optical emission (green) are brighter near the central regions where the x-rays seem to be absorbed by denser, cooler material on the side of the expanding debris cloud facing the Earth. Located in the neighboring galaxy known as the Large Magellanic Cloud, the apparent age of this supernova remnant is between 2,000 and 5,000 years, its extended glow spanning about 60 light-years. The intriguing image is a composite of x-ray data from the orbiting Chandra Observatory, optical data from the Hubble Space Telescope, and radio from the Australia Telescope Compact Array.
\ この感動を宇宙仲間にシェア /
宇宙をXでシェア
© NASA / APOD